Check out our latest products
The ICs enhance lithium-ion battery safety with overcharge prevention, temperature monitoring, RTC support, and simplified assembly. Learn more!

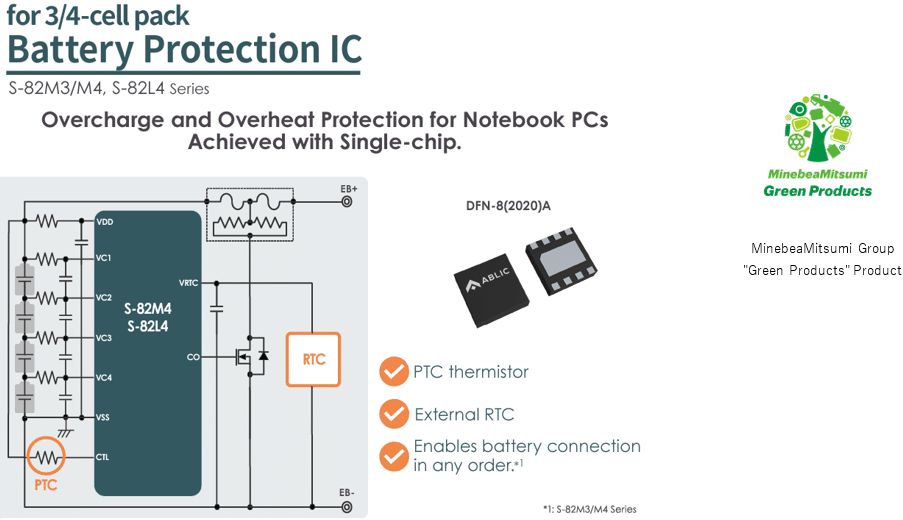
ABLIC, a group company of MinebeaMitsumi Inc., has announced the launch of secondary protection ICs for lithium-ion batteries: the S-82M3/M4 Series, designed for notebook PC battery packs with three serially connected cells, and the S-82L4 Series, intended for packs with three to four serially connected cells.
Secondary protection ICs safeguard lithium-ion batteries from overcharging by working with a protection fuse, which activates upon receiving an external signal. These ICs also meet requirements for temperature protection and real-time clock (RTC) drive by monitoring abnormal battery temperatures and providing a constant-voltage output for RTC operation through an external PTC thermistor.

The Series includes two models: the S-82M3 for 3-cell packs and the S-82M4 for 4-cell packs. Both models feature a wake-up function that prevents protection fuses from blowing during battery pack assembly. This ensures the fuse activation signal is issued only after all batteries are connected, regardless of the sequence, simplifying the assembly process.
The S-82L4 Series works with both 3-cell and 4-cell packs but lacks the wake-up function of the S-82M3/M4 Series.
Both series share key features, including:
- A CTL pin that supports temperature detection via a PTC thermistor, enabling overcharge and temperature protection in a single unit.
- A constant-voltage output circuit with a minimum voltage of 1.5 V to power an external RTC, eliminating the need for a coin-type battery for RTC backup.
- A compact DFN-8(2020)A package design with the back of the package used as a pin, reducing circuit board footprint.
The constant-voltage output circuit allows direct power supply from the main battery, even when the PC is shut down. It stops operating when the battery voltage reaches the shutdown threshold, and the IC enters a low-current consumption mode, reducing overall power usage.
For more information, click here.


![[5G & 2.4G] Indoor/Outdoor Security Camera for Home, Baby/Elder/Dog/Pet Camera with Phone App, Wi-Fi Camera w/Spotlight, Color Night Vision, 2-Way Audio, 24/7, SD/Cloud Storage, Work w/Alexa, 2Pack](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/71gzKbvCrrL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)



![[3 Pack] Sport Bands Compatible with Fitbit Charge 5 Bands Women Men, Adjustable Soft Silicone Charge 5 Wristband Strap for Fitbit Charge 5, Large](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/61Tqj4Sz2rL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)