Check out our latest products
Need accurate current and voltage control for battery testing or power supplies? This reference design solves regulation errors and startup issues—see more!
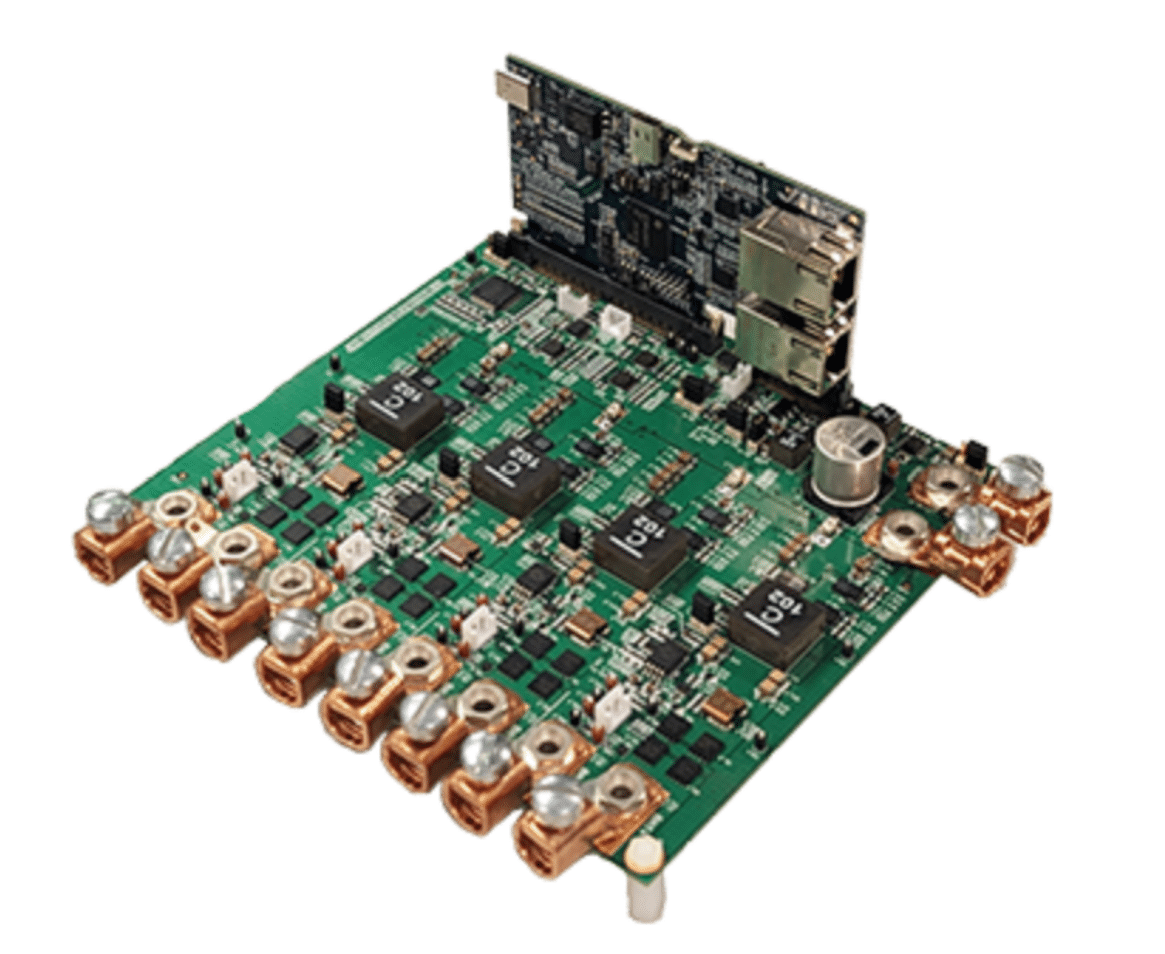
The TIDA-010090 reference design from Texas Instruments (TI) provides design engineers with a solution for precise current and voltage control in a bidirectional buck converter power stage. Using a C2000 real-time microcontroller (MCU) and a precision ADC ADS8588S, this design achieves a current regulation error of less than ±10mA and a voltage regulation error of ±1mV by leveraging the high-resolution pulse-width modulation (PWM) peripheral of the C2000 MCU. This reference design is particularly useful for battery cell formation, test equipment, and programmable DC power supplies.
Engineers on battery testing systems can use this design to develop equipment capable of evaluating single cells, battery modules, and high-voltage battery packs. These systems require precision power supplies and data acquisition capabilities to support charging, discharging, and parameter measurement. The reference design also supports the formation stage of Li-Ion battery manufacturing, where controlled charge and discharge cycles create the solid electrolyte interface (SEI) layer, a key factor in battery performance and longevity. Battery formation systems built using this design can achieve voltage and current accuracy between ±0.02% and ±0.05% of full scale.

The design enables engineers to implement a high-resolution PWM control system using the TMS320F28P650DK MCU, which manages current and voltage regulation. The INA241 current sense amplifier measures battery current, while the OPA2186 operational amplifier measures battery voltage. The ADS8588S ADC converts these signals into digital data for precise control, and the C2000’s on-chip window comparators provide overcurrent protection.
The design employs a cascaded voltage and current loop for consistent charging and discharging control. When the battery voltage is significantly below the constant-voltage setting (VSET), the voltage loop maintains a constant-current setting (ISET). As the voltage nears VSET, the system reduces ISET to prevent overshooting the voltage limit. This approach ensures reliable operation in both charge and discharge modes, with VSET as a safeguard against overcharging and excessive discharge.

To prevent current overshoot during startup, engineers can implement one of two methods. The first method involves keeping the output relay open until the buck converter reaches a voltage close to the battery voltage, preventing sudden inrush currents. The second method starts the buck converter in discontinuous conduction mode (DCM), keeping the low-side switch OFF during charging or the high-side switch OFF during discharging before transitioning to synchronous mode using a timer.
TI has tested this reference design. It comes with a bill of materials (BOM), schematics, assembly drawing, printed circuit board (PCB) layout, and more. The company’s website has additional data about the reference design. To read more about this reference design, click here.


![[5G & 2.4G] Indoor/Outdoor Security Camera for Home, Baby/Elder/Dog/Pet Camera with Phone App, Wi-Fi Camera w/Spotlight, Color Night Vision, 2-Way Audio, 24/7, SD/Cloud Storage, Work w/Alexa, 2Pack](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/71gzKbvCrrL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)



![[3 Pack] Sport Bands Compatible with Fitbit Charge 5 Bands Women Men, Adjustable Soft Silicone Charge 5 Wristband Strap for Fitbit Charge 5, Large](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/61Tqj4Sz2rL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)