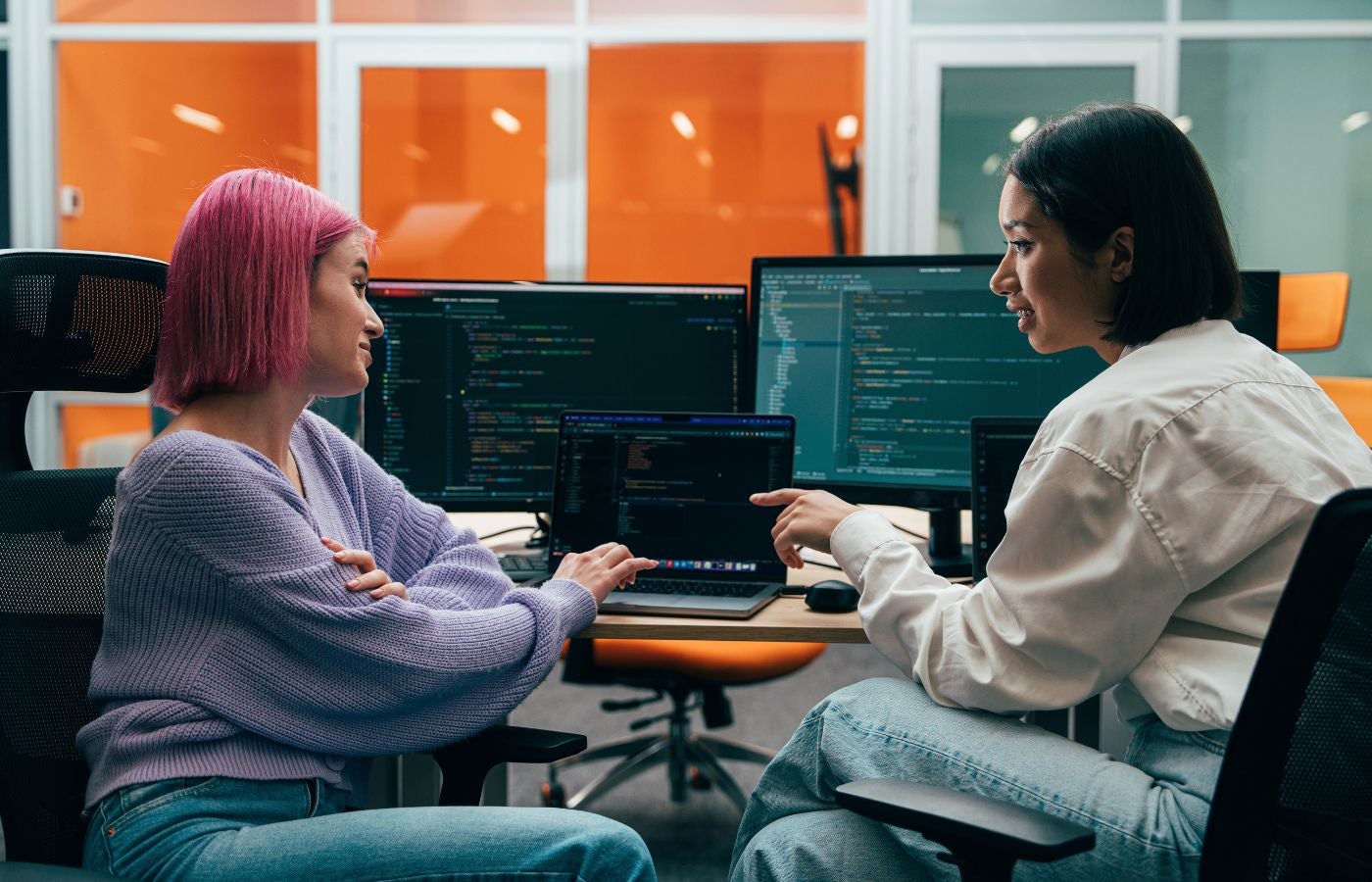
Check out our latest products
Researchers from RWTH Aachen University have disassembled two major companies’ EV batteries to uncover hidden design details, offering insight into the technology behind the two companies.
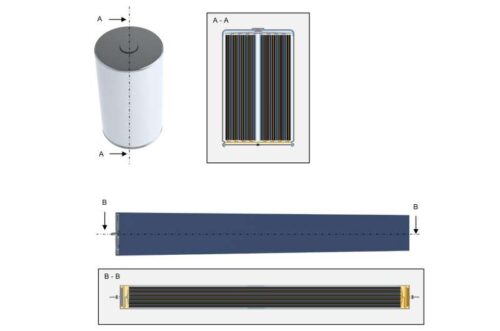
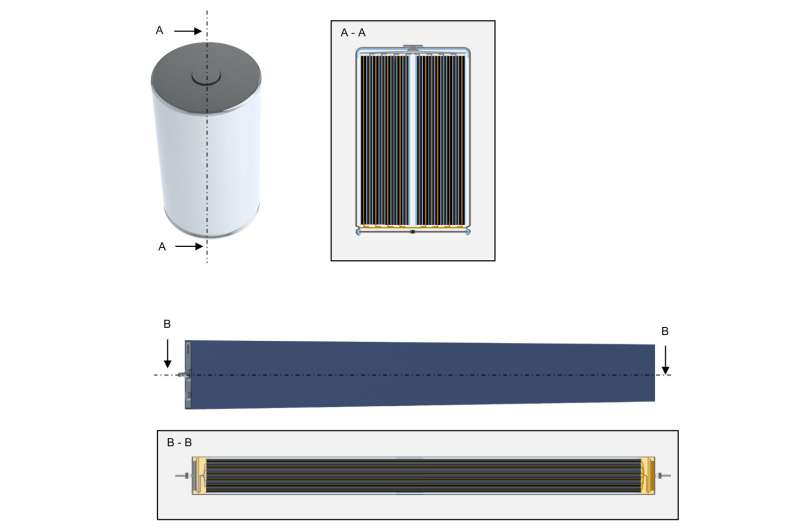
Two major companies dominate the EV market: Tesla, which is most popular in Europe and North America, and BYD, which leads in China. Both have shared little information about their battery designs, leaving key details unknown. To compare their batteries and gain insight into EV battery technology, researchers from RWTH Aachen University in Germany have disassembled one from each company.
Findings published in Cell Reports Physical Science show that Tesla’s batteries focus on high energy density and performance, while BYD’s prioritize space efficiency and lower-cost materials. The study found BYD’s battery to be more efficient due to its better thermal management.

To investigate this, researchers examined Tesla’s 4680 cell and BYD’s Blade cell, analyzing their design and performance. They studied the mechanical structure, dimensions, electrode materials, and electrical and thermal performance of each battery. Additionally, they identified the assembly processes and estimated material costs.
The study revealed significant differences in how the two batteries charge and discharge relative to their maximum capacity.
Researchers found that BYD’s Blade cell secures electrode sheets differently, using an electrode stack with a unique laminated separator between the anode and cathode. Tesla’s 4680 cell, on the other hand, features a novel binder that differs from those commonly used in the industry.
Despite these differences, both batteries share unexpected similarities. Both use laser welding instead of the more common ultrasonic welding to connect their thin electrode foils. Additionally, even though the BYD cell is much larger than Tesla’s, the proportion of passive components—such as current collectors, housing, and busbars—is similar.
The researchers stated that the findings demonstrate two different battery design approaches. Further research is needed to examine how these mechanical design choices affect electrode performance and battery lifespan.
Reference: Jonas Gorsch et al. Contrasting a BYD Blade prismatic cell and Tesla 4680 cylindrical cell with a teardown analysis of design and performance, Cell Reports Physical Science (2025). DOI: 10.1016/j.xcrp.2025.102453. www.cell.com/cell-reports-phys … 2666-3864(25)00052-9


![[5G & 2.4G] Indoor/Outdoor Security Camera for Home, Baby/Elder/Dog/Pet Camera with Phone App, Wi-Fi Camera w/Spotlight, Color Night Vision, 2-Way Audio, 24/7, SD/Cloud Storage, Work w/Alexa, 2Pack](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/71gzKbvCrrL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)



![[3 Pack] Sport Bands Compatible with Fitbit Charge 5 Bands Women Men, Adjustable Soft Silicone Charge 5 Wristband Strap for Fitbit Charge 5, Large](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/61Tqj4Sz2rL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)