Check out our latest products
Machine vision is critical for automation and Artificial Intelligence (AI). But how are new components and modules making development of Machine Vision systems faster, better and more intelligent? Let’s find out…
When machine vision first emerged, it seemed like science fiction had come to life. The idea of machines being able to “see” and interpret images felt groundbreaking, yet manufacturers were initially hesitant to embrace it. A combination of limited awareness and the steep costs of implementation held back its widespread adoption. However, over time, machine vision has proven its value, and the landscape has shifted dramatically.
Machine vision systems, which use cameras, sensors, and sophisticated algorithms to process visual data, have revolutionized industries by improving precision, efficiency, and output. From its early days, machine vision has become an integral part of various applications, from barcode identification to texture analysis, and it’s continuing to evolve. As the technology becomes more accessible and capable, its role in shaping Industry 4.0 and the future of smart manufacturing is undeniable. The integration of machine vision with artificial intelligence and collaborative robots is opening new doors for increased automation, improved quality control, and optimized operations.
Today, machine vision is not just a tool for inspection but a key component of the digital transformation in industries. It enables automated systems to detect defects, reduce human error, and enhance decision-making with real-time visual data. As this technology matures, it promises to revolutionize the way we work, offering new opportunities for smarter, more efficient manufacturing processes.
Cameras: Smaller Yet Better
The demand for high-quality visual content is rising across industries, driven by advances in embedded vision systems. From industrial inspection to smart traffic monitoring, these systems rely on sharp, clear images for accurate performance. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) algorithms, in particular, need precise visual input for tasks like object detection, classification, and defect recognition—low-quality images simply aren’t enough. As a result, high-resolution sensors have become essential.
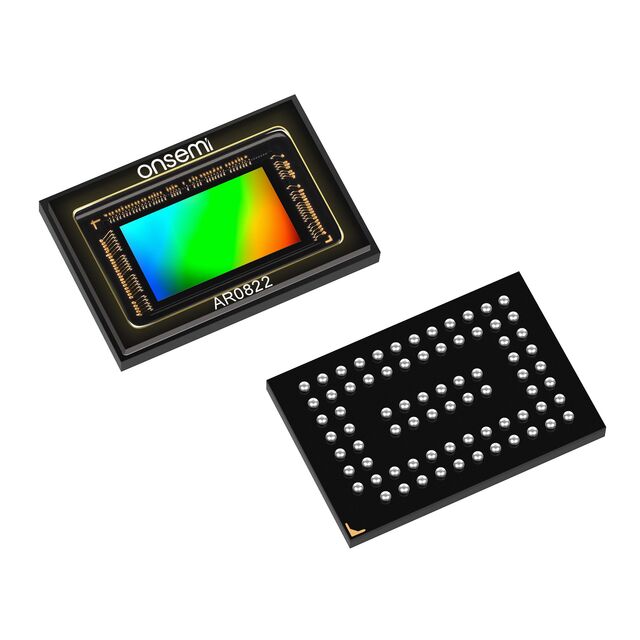
Where 1MP to 5MP cameras once sufficed, today’s systems often require 8MP or higher to support advanced surveillance and analytics. The AR0822NPSC10SMTA0-DR (8 MP CMOS Image Sensor) from Onsemi meets these needs, delivering detailed imagery for precision-critical applications like robotics and inspection.
This trend is supported by rapid improvements in processing and connectivity. Modern embedded processors now handle the heavy data load of high-res sensors without compromising performance. Interfaces like Mobile Industry Processor Interface (MIPI) and Gigabit Multimedia Serial Link 2 (GMSL 2), along with 5G and improved storage, streamline the transfer and access of high-resolution image data. As high-res displays become more widespread, demand for high-fidelity image capture also grows.
For applications requiring both detail and color accuracy—such as medical imaging and quality control—you need cameras that offer precision to detect subtle variations and ensure accuracy such as Delta Electronics’ DMV-CL12MGC008, which is a 12 MP Colour Machine Vision Camera
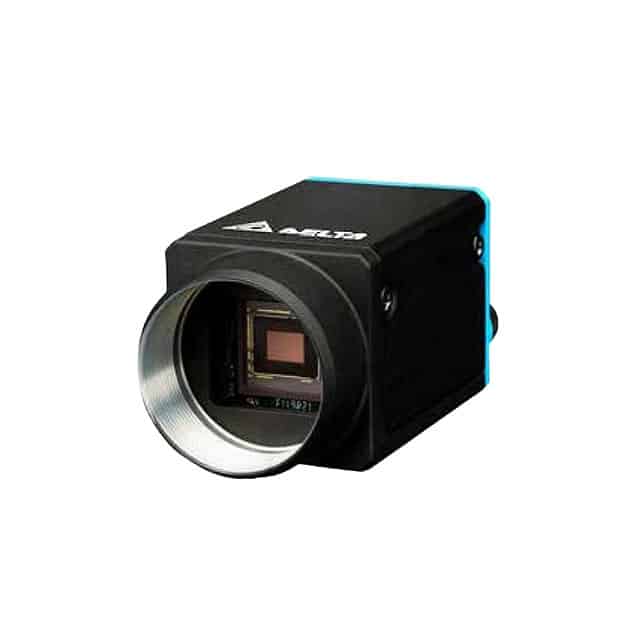

But are even higher cameras even better? Balvinder Singh, Director of JB Instruments pointed out that, “While many assume higher megapixels like 30 or 40 MP are required, he clarified that 8 to 12 MP cameras are typically sufficient for most industrial applications.”
But resolution alone doesn’t guarantee clarity. Sensor architecture, lens quality, and features like global shutters all play key roles. Larger or more advanced sensors reduce noise and improve sensitivity, while optical quality helps preserve image integrity. These factors are especially important in compact setups like wearable devices or smart electronics. For such space-limited environments, the NanEyeM Miniature Camera Module (RGB) from ams Osram offers strong imaging performance in a compact form.
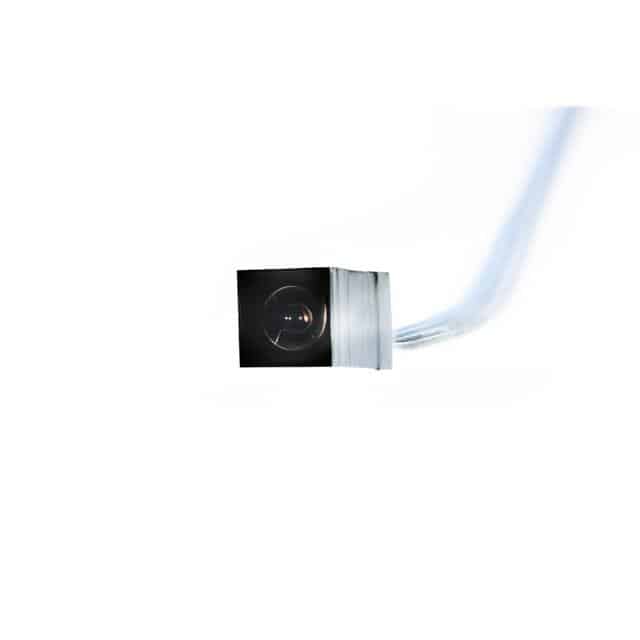

ToF Sensors: Seeing in 3D
Time-of-Flight (ToF) technology has become essential in warehouse automation, where mobile robots like Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs) and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) operate in complex, fast-paced environments. Once cutting-edge, ToF cameras now provide real-time 3D imaging, replacing traditional methods like stereo vision, which require textured surfaces and careful calibration.
“ToF sensors offer another layer of capability. These sensors detect how long it takes for light to bounce back from an object, enabling them to identify fast-moving items in real time—such as a bird flying past. While similar in function to laser sensors, ToF sensors are faster and better suited for dynamic environments,” Somnnath Bera, Ex. General Manager, NTPC
ToF cameras use three core components: a light source, a sensor, and a processing unit. They measure how long it takes for light to reflect off objects and return, enabling fast, accurate distance calculations in any lighting—whether total darkness or bright warehouse conditions. Devices like the ADTF3175BMLZ (1 MP Time-of-Flight Depth Module) from Analog Devices (ADI) offer real-time depth mapping, ideal for gesture recognition and obstacle detection in dynamic settings.
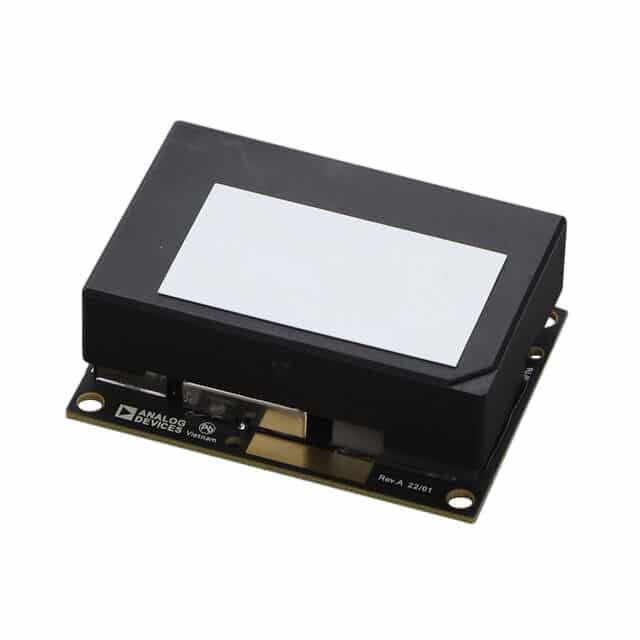

A key advantage of ToF in indoor spaces is GPS-free localization. Robots can reference known map points and use triangulation to determine their position. In new environments, ToF cameras support Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) to build 3D maps on the fly, enabling safe navigation even in changing layouts. High-precision models like the MLX75026RTH-AAA-110-SP (3D Time-of-Flight Sensor) from Melexis Technologies NV further enhance mapping, supporting both industrial and AR/VR applications.
ToF also improves navigation and obstacle avoidance by providing a live 3D view of the surroundings. Robots can detect obstacles and adjust their paths in real time, improving safety and minimizing downtime. In large areas such as logistics hubs, RealSense Depth Camera D455 (Long-Range) from Intel RealSense helps detect distant objects and ensure smooth movement across wide spaces.
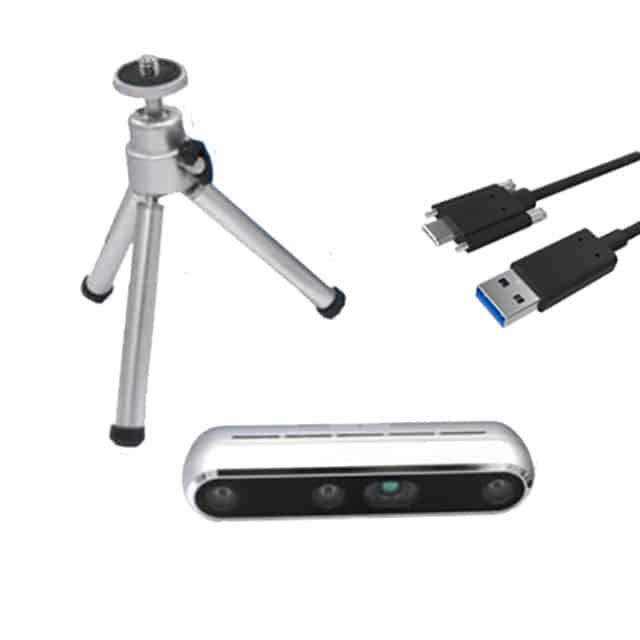

For object detection, ToF systems outperform monocular AI cameras by recognizing 3D shapes and matching them to stored profiles. This enables robots to take appropriate actions without relying on complex machine learning models. “In automotive or other complex parts that require depth assessment, 3D cameras are essential to detect faults accurately,” Murali Chandrahasan, Senior Director- Intelligent Industry, Capgemini Invent.
Edge AI: Adding Intelligence
A major advancement in machine vision is its integration with edge AI, where visual data is processed directly on the device rather than in the cloud. This reduces latency, saves bandwidth, and improves reliability—especially in areas with limited connectivity. For example, a security camera with edge AI can detect intrusions instantly, without relying on remote servers.
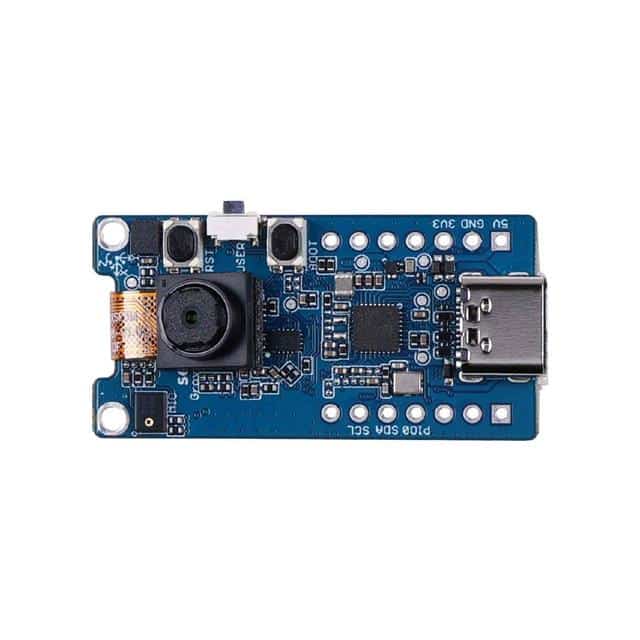
A prime example is the Grove – OV2640 Sensor (Vision AI Camera) from Seeed Studio which combines image capture and AI inference in one unit. It enables fast, on-the-spot decision-making in security, retail, and factory automation, cutting the need for external processing and speeding up response times.
Edge-based machine vision also strengthens privacy. In healthcare, portable devices can analyze X-rays or skin conditions locally, keeping patient data secure. In retail, shelf-monitoring systems process images on-site, ensuring compliance with data regulations.
Usability is improving too. With natural language processing, vision systems can interpret labels or follow simple instructions, making automation accessible to non-technical users in industrial and commercial settings.
“As the AI-integrated system continues to receive more data over time, its accuracy in detecting mismatches improves significantly. We’ve successfully applied this approach in scenarios like incoming material inspection, and the same methodology can be extended to validate outgoing products as well,” explained Murali.
Balvinder highlighted, “AI becomes especially useful in manual production environments, where it provides consistent, automated judgement on whether a part has been produced within the defined specifications. Many automotive manufacturers, such as Honda, Hero, and Maruti, rely on these systems. For instance, when producing components like car steering units, the AI vision system can validate the dimensions before shipment, ensuring that the parts delivered meet client standards.”
Looking ahead, advanced vision systems may exceed human perception—allowing robots to navigate complex spaces, perform precise tasks, and make decisions autonomously. As machine vision evolves, it will continue to drive smarter, faster, and more efficient operations across manufacturing, healthcare, retail, and beyond.
Seeing the Invisible
Machine vision has moved far beyond visible light, using non-visible imaging to solve complex inspection and analysis challenges. Technologies like infrared (IR), ultraviolet (UV), and short-wave infrared (SWIR) are now essential across industries, enabling capabilities that traditional systems cannot offer.
Infrared imaging captures heat signatures, making it valuable for detecting temperature changes in equipment, buildings, or environments. Applications range from energy audits to intrusion detection. The MLX90640ESF-BAB-000-TU (32×24 IR Thermal Imager) from Melexis Technologies NV, for example, is a compact tool ideal for spotting heat loss, equipment faults, or intruders—even in total darkness. Its small size and reliability make it effective for both automated systems and portable inspections.
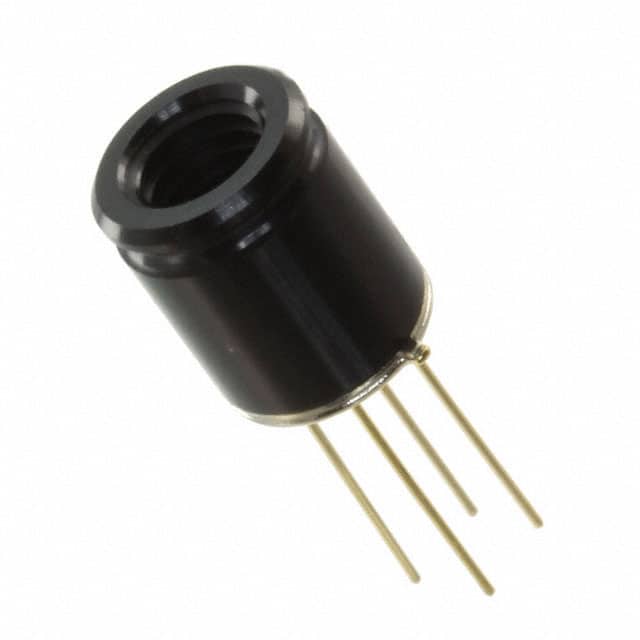

Ultraviolet imaging is used to reveal surface defects, contaminants, or markings invisible under standard lighting. Industries such as semiconductors, food processing, and packaging rely on UV to identify fine cracks, residues, or counterfeit indicators that regular lighting would miss.
SWIR imaging opens up inspection beyond visible and thermal ranges. With wavelengths between 900–1700 nm, it can see through silicon, plastics, and organic materials. SWIR is used in electronics for wafer inspection, in agriculture for detecting bruises in fruit, and in recycling for sorting materials based on composition. Its ability to detect internal flaws without damaging the object is key in quality-critical environments.
These imaging methods each require specific sensors, lighting, and optics. Without the right hardware setup, their full potential can’t be realized. Success in non-visible imaging depends on using purpose-built components designed for each spectrum. As demand grows for better accuracy and reliability, these technologies will continue to drive innovation in machine vision.
What’s Next?
Generative AI is transforming computer vision, particularly through synthetic data creation. It generates outputs across domains like text-to-image, text-to-video, and text-to-audio, which can be used to train systems for tasks like facial recognition and object detection. This reduces privacy risks and speeds up training by automating data labeling.
New imaging technologies, such as hyperspectral and multispectral imaging, capture data beyond visible light, offering detailed insights in sectors like agriculture, healthcare, and environmental monitoring. The integration of 3D computer vision and Light Detection and Ranging (LiDAR) will enhance spatial awareness in urban planning and logistics.
Neuromorphic vision sensors, which detect changes in a scene, are ideal for real-time applications like robotics and autonomous systems. These sensors offer energy efficiency and fast processing, making them suitable for wearable devices and drones.
As the demand for higher resolution, non-visible spectrum imaging, and advanced analytics grows, machine vision will continue to push the boundaries of what’s possible, offering smarter solutions and accelerating the digital transformation across diverse sectors. With the advent of emerging technologies like generative AI and neuromorphic vision sensors, the future of machine vision holds even greater potential for innovation and progress.
Components Featured in This Article: Specs & Links to Purchase
| Category | Component Name | Specs | Brand | Buy Now |
| Image Sensor | AR0822NPSC10SMTA0-DR | CMOS, 8 MP | Onsemi | click here |
| Camera Module | DMV-CL12MGC008 | 12 MP Colour | Delta Electronics | click here |
| Camera Module | NanEye | Micro Camera Module (RGB) | ams Osram | click here |
| Time-of-Flight Sensor | ADTF3175BMLZ | 1 MP, Depth Module | Analog Devices (ADI) | click here |
| Time-of-Flight Sensor | MLX75026RTH-AAA-110-SP | 3D | Melexis Technologies NV | click here |
| Camera Module | RealSense Depth Camera D455 | 6DOF, Stereo Depth Module | Intel RealSense | click here |
| Edge AI Camera | Grove-OV2640 | Compact AI camera sensor | Seeed Studio | click here |
| Thermal Imaging Module | MLX90640ESF-BAB-000-TU | 32×24 IR | Melexis Technologies NV | click here |


![[5G & 2.4G] Indoor/Outdoor Security Camera for Home, Baby/Elder/Dog/Pet Camera with Phone App, Wi-Fi Camera w/Spotlight, Color Night Vision, 2-Way Audio, 24/7, SD/Cloud Storage, Work w/Alexa, 2Pack](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/71gzKbvCrrL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)



![[3 Pack] Sport Bands Compatible with Fitbit Charge 5 Bands Women Men, Adjustable Soft Silicone Charge 5 Wristband Strap for Fitbit Charge 5, Large](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/61Tqj4Sz2rL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)