Check out our latest products
Drainage systems are vital for storm water management but often transport pollutants, especially plastics, to rivers and oceans, harming ecosystems. Traditional sewer cleaning methods include manual labour, hydraulic flushing, and chemical cleaners.
Instead, this DIY sewer drain shield system, combining ultrasonic sensors, GSM modules, nets, and PVC pipes, reduces debris entering drainage systems, thus ensuring cleaner, more efficient operations.
This solution is low-maintenance, labour-saving, and supports sustainable waste management. It aligns with the Central government’s Clean India initiative, integrating smart waste management to protect water bodies. The bill of materials is detailed in the table on previous page.

| Bill of Materials | |
| Components | Quantity |
| Arduino Uno board (MOD1) | 1 |
| GSM module SIM800L (MOD2) | 1 |
| Ultrasonic sensor module (S1) | 1 |
| USB cable (for connecting 5V) | 1 |
| Plastic waste | As required |
| Wooden ply | As required |
| PVC pipe | As required |
| Net | As required |
Sewer Drain Shield – Circuit and Working
Fig. 1 shows the circuit diagram of the proposed drain shield for smart cities. It is built around an Arduino Uno board (MOD1), GSM module SIM800L (MOD2), an ultrasonic sensor module (S1), and a few other components.

The Arduino software is used to develop this system. This software is compatible with any Arduino board. The Arduino Uno IDE makes it easy to write code and upload it to the board.

In the source code, the serial pins are defined for the GSM module, and the baud rate is set. The default baud rate of the SIM800L is 4800 for most modules. The phone number is then set to receive an SMS notification when a drain blockage is detected. The distance is measured to check for blockages in the drain net.
This distance is used to create a function that notifies the department by making a call to the designated number to clear the waste collected in the net. Fig. 2 shows a code snippet setting the pins and phone number for the sensor. Fig. 3 shows the code snippet for making the phone call.


Also Check: Unique DIY Arduino Projects
Construction and Testing
The phone number to receive the SMS should be included in the source code. After that, the source code may be uploaded to the Arduino Uno board. Once the circuit is assembled based on the diagram in Fig. 1, the system can be powered on.
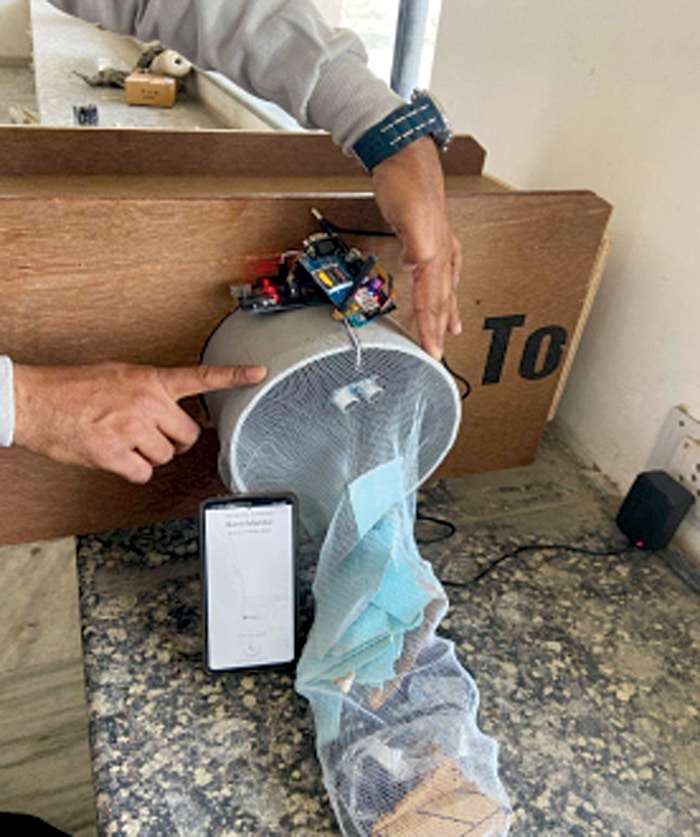
When the distance detected by the ultrasonic sensor is less than the threshold value (blocking distance from the sensor), the system will attempt to make a call using the GSM module to the set number. After a few seconds, the call will hang up. The authors’ prototype is shown in Fig. 4.

After assembling the system correctly, it should be installed into the drainage system. After proper installation of the net into the sewer pipe, the ultrasonic sensor should be attached in such a way that it checks the distance for blockages in the drain net. It collects plastic and other waste in the net, as shown in Fig. 4. When a blockage occurs, the sensor activates and sends an SMS to the responsible person or authority.
For testing purposes, placing a hand in front of the ultrasonic sensor will simulate a drain blockage. However, in actual deployment, the system’s circuit and sensor should be properly waterproofed and dustproofed using appropriate coatings.
Denis Jangeed (left), M.Tech, B.Tech, is Assistant Professor at Department of Civil Engineering, while Yogesh Kumar Jatav (right), B.Tech, is Design Engineer (CII) at Geetanjali Institute of Technical Studies, Udaipur.


![[5G & 2.4G] Indoor/Outdoor Security Camera for Home, Baby/Elder/Dog/Pet Camera with Phone App, Wi-Fi Camera w/Spotlight, Color Night Vision, 2-Way Audio, 24/7, SD/Cloud Storage, Work w/Alexa, 2Pack](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/71gzKbvCrrL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)



![[3 Pack] Sport Bands Compatible with Fitbit Charge 5 Bands Women Men, Adjustable Soft Silicone Charge 5 Wristband Strap for Fitbit Charge 5, Large](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/61Tqj4Sz2rL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)