Check out our latest products
The model reveals how lithium plating starts during fast charging, offering insights that could lead to safer, longer-lasting lithium-ion batteries used in many devices.
Fast-charging lithium-ion batteries are used in everything from phones and laptops to electric vehicles—but they’re also known for risks like overheating and fire. Researchers at the University of Wisconsin–Madison have developed a new computational model that offers fresh insight into one of the key reasons these batteries fail.
The model explains how lithium plating occurs—a process where metallic lithium forms on the battery’s anode during fast charging, leading to quicker degradation or even fire. This understanding could help make fast-charging batteries safer and more durable.

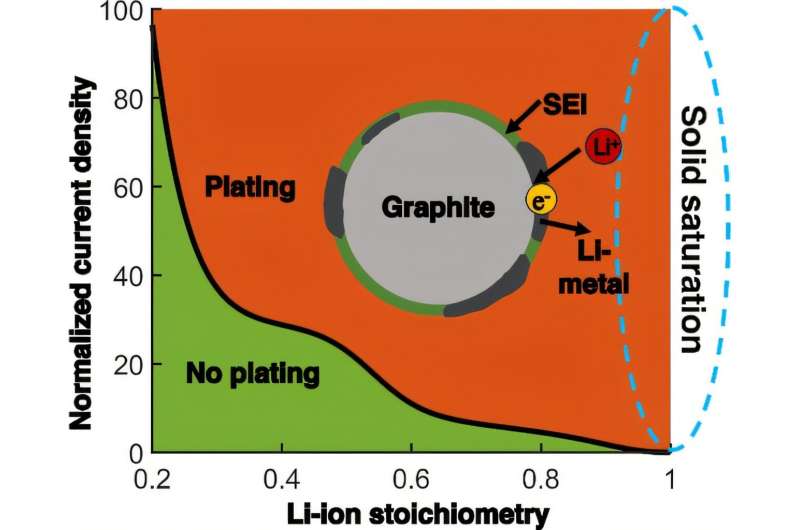
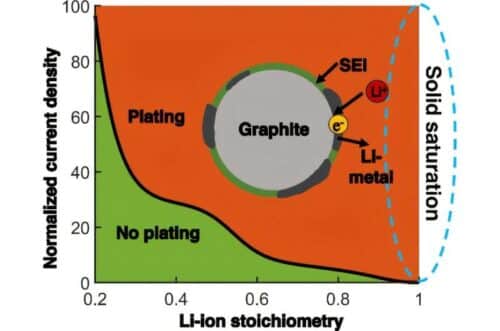
The mechanisms behind lithium plating in fast-charging lithium-ion batteries have remained unclear until recently. A new computational model has now been used to study this process on a graphite anode, revealing how the interaction between ion transport and electrochemical reactions leads to lithium plating.
The findings highlight key relationships between operating conditions, material properties, and the onset of lithium plating. Based on these results, a physics-based diagram was developed to guide strategies for reducing plating. This tool allows other researchers to apply the insights without conducting additional simulations.
The results can inform the design of both battery materials and optimized charging protocols aimed at extending battery life. One key application is adjusting current densities during charging, depending on the state of charge and material characteristics, to prevent plating.
While earlier research has mostly focused on extreme cases of lithium plating, this model offers a broader view, enabling investigation across a wider range of conditions. Future work will expand the model to include mechanical factors, such as stress, to further understand their role in lithium plating.
Reference: Weiyu Li, Onset of Lithium Plating in Fast-Charging Li-Ion Batteries, ACS Energy Letters (2025). DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.5c00322


![[5G & 2.4G] Indoor/Outdoor Security Camera for Home, Baby/Elder/Dog/Pet Camera with Phone App, Wi-Fi Camera w/Spotlight, Color Night Vision, 2-Way Audio, 24/7, SD/Cloud Storage, Work w/Alexa, 2Pack](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/71gzKbvCrrL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)



![[3 Pack] Sport Bands Compatible with Fitbit Charge 5 Bands Women Men, Adjustable Soft Silicone Charge 5 Wristband Strap for Fitbit Charge 5, Large](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/61Tqj4Sz2rL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)