Check out our latest products
A 60GHz radar design enhances in-cabin sensing with child presence detection, occupancy sensing, and more. Read on to know more!
Texas Instruments (TI) have launched TIDEP-01037, a compact, low-power reference design built around the AWRL6432, a single-chip 60GHz automotive radar sensor. Designed for in-cabin applications, this high-performance radar system enables features like Child Presence Detection (CPD), Intruder Detection (ID), occupancy sensing, driver vital sign monitoring, and seat belt reminders. By leveraging machine-learning algorithms, the automotive radar sensor enhances safety and security by accurately detecting and classifying vehicle occupants. With its small form factor and optimized RF performance, this design provides an efficient solution for next-generation automotive sensing applications.
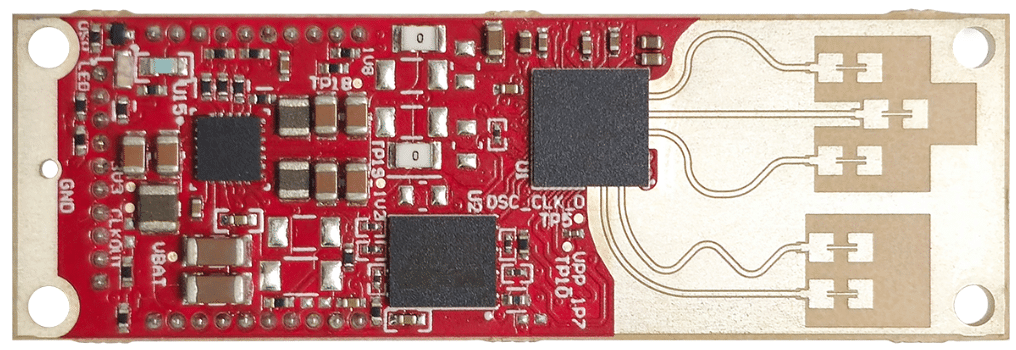
The design’s small form factor allows easy evaluation and integration into end applications. The radar sensor operates using Frequency-Modulated Continuous Wave (FMCW) technology, utilizing two transmitter antennas for transmission and three receiver antennas for reception. This enables the radar system to capture data on distance, angle, and velocity, allowing it to detect motion and presence.

The single-chip 60GHz automotive radar sensor is powered by three voltage rails in a power-optimized topology, supplied by the PMIC, which converts a 12V battery input. The use of a single PMIC helps achieve a compact design, with the 12V input connecting all three connectors. The reference design also features an onboard CAN PHY for communication with external automotive networks and supports SPI-based raw data capture.
The design provides a ready-to-use, compact mmWave in-cabin radar sensor with a cost-optimized bill of materials. The board’s antennas offer a 120° field of view in both azimuth and elevation, 3.5GHz bandwidth, and 6-7dBi peak gain, utilizing high-performance Rogers RO3003 material.

The reference design incorporates TI’s low-cost, compact, low-power Derby PMIC and CAN PHY. It features onboard connectors that support multiple communication interfaces, including UART, RS232, SPI, CAN, LIN, JTAG, I2C, and GPIOs. The PMIC includes three step-down converters that run in forced PWM mode by default but can be configured to operate in AutoPFM mode. This reference design aims to provide a compact, ready-to-use radar module for in-cabin applications. The board, including mounting holes, measures approximately 18mm × 55mm.
In-cabin applications require the radar device to be mounted in an optimal position for effective coverage. Manufacturers explore various mounting options, such as center overhead, front, side-pillar, and second-row overhead mounts, to maximize coverage. This reference design is specifically designed for a front overhead mount, enabling two-row coverage.
The reference design features onboard etched-patch antennas for three receivers and two transmitters, providing a wide field of view (FOV) in both azimuth and elevation with high gain and good bandwidth coverage.
TI has tested this reference design. It comes with a bill of materials (BOM), schematics, assembly drawing, printed circuit board (PCB) layout, and more. The company’s website has additional data about the reference design. To read more about this reference design, click here.


![[5G & 2.4G] Indoor/Outdoor Security Camera for Home, Baby/Elder/Dog/Pet Camera with Phone App, Wi-Fi Camera w/Spotlight, Color Night Vision, 2-Way Audio, 24/7, SD/Cloud Storage, Work w/Alexa, 2Pack](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/71gzKbvCrrL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)



![[3 Pack] Sport Bands Compatible with Fitbit Charge 5 Bands Women Men, Adjustable Soft Silicone Charge 5 Wristband Strap for Fitbit Charge 5, Large](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/61Tqj4Sz2rL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)