Check out our latest products
Supporting wireless protocols like Sub-1 GHz, BLE, and NB-IoT, this solution maximizes battery life while ensuring reliable connectivity for IoT-enabled utility applications.
Smart utility meters powered by batteries—such as gas, water, and heat meters—present a growing opportunity for wireless communication technologies, including Sub-1 GHz, Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE), NB-IoT, and others. Each of these protocols comes with trade-offs in terms of range, data rate, and power efficiency. Sub-1 GHz, for example, delivers communication ranges of up to 1600 meters with data rates reaching 500 kbps, making it suitable for applications like utility metering, smoke detectors, and building-based temperature sensors. For applications requiring higher data throughput, BLE at 2.4 GHz may be more appropriate. BLE offers data rates up to 2 Mbps and range from 200 to 400 meters in long-range mode, while maintaining ultra-low power consumption that allows it to operate for years on a coin cell. Its broad applicability spans from medical wearables to consumer peripherals, making it one of the most widely used low-power wireless protocols.
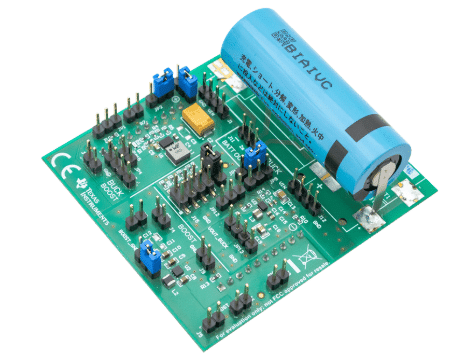
This reference design TIDA-010053 by Texas Instruments (TI) presents an efficient, battery-powered solution tailored for wireless-enabled smart meters and IoT applications. The design supports various wireless technologies, including Sub-1 GHz, BLE, and NB-IoT, and integrates three key power supply topologies: buck, boost, and buck-boost converters. These are optimized for battery-operated devices using lithium manganese dioxide (LiMnO₂) primary cells and can be implemented alongside commercial off-the-shelf narrowband communication modules.

A core component of this reference design is the Battery and System Health Monitoring hardware (TIDA-01546), which enables accurate State-of-Health (SOH) measurement of the battery. An always-on current sensing mechanism captures RF transmission peaks and schedules SOH measurement with an adjustable delay to ensure efficiency and battery longevity. The power converters—TPS63900, TPS610995, and TPS62840—demonstrate high efficiency even under light loads, which is vital for extending the operating life of smart metering devices. For example, the TPS63900 buck-boost converter delivers over 90% efficiency at just a 10-µA load with an extremely low quiescent current of 75 nA. It also features dynamic voltage scaling, allowing applications to shift between two output voltages to optimize power during active and standby modes.
The TPS610995 boost converter supports up to 1 A output current with 400 nA typical quiescent current and is well-suited for applications requiring high efficiency under light loads. Similarly, the TPS62840 step-down (buck) converter uses TI’s DCS-Control™ topology to maintain high efficiency even in the microampere range during Power-Save Mode.

Target applications include gas, water, heat, and cold meters; cellular module asset tracking; sensor tags; fault indicators; and automated meter reading (AMR) systems powered by primary cells. This comprehensive, low-power reference design ensures scalable performance for RF-enabled metering and IoT solutions.
TI has tested this reference design. It comes with a bill of materials (BOM), schematics, assembly drawing, printed circuit board (PCB) layout, and more. The company’s website has additional data about the reference design. To read more about this reference design, click here.


![[5G & 2.4G] Indoor/Outdoor Security Camera for Home, Baby/Elder/Dog/Pet Camera with Phone App, Wi-Fi Camera w/Spotlight, Color Night Vision, 2-Way Audio, 24/7, SD/Cloud Storage, Work w/Alexa, 2Pack](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/71gzKbvCrrL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)



![[3 Pack] Sport Bands Compatible with Fitbit Charge 5 Bands Women Men, Adjustable Soft Silicone Charge 5 Wristband Strap for Fitbit Charge 5, Large](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/61Tqj4Sz2rL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)