Check out our latest products
A way to shrink pixels to unprecedented sizes using perovskite, potentially revolutionizing display technology and paving the way for ultra-high-resolution, ultra-compact screens that could redefine the limits of modern display technology.

A team of physicists, engineers, and photonics specialists from Zhejiang University, China, along with colleagues from the University of Cambridge, U.K., have developed a method to create pixels as small as a virus. Their findings highlight the potential of perovskite as a game-changer in display technology.
The push for miniaturization in electronics has driven innovation for decades. In computing, the goal has long been to increase transistor density on integrated circuits. Likewise, reducing pixel size in displays has enhanced image sharpness. However, current micro-LED technology, based on II-V semiconductors, has reached a practical limit due to cost and efficiency constraints. This challenge led researchers to explore alternative materials—specifically, perovskite.

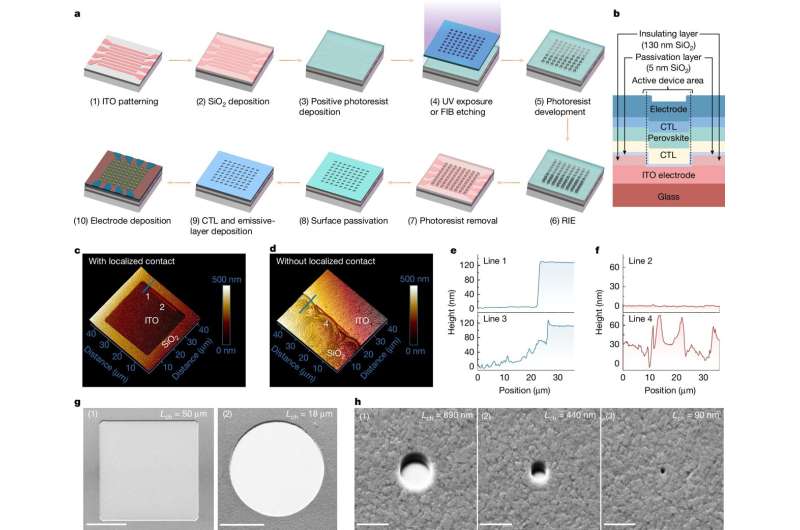
Perovskite, widely studied as a cost-effective alternative to silicon in solar cells, proved promising for display applications. The team successfully fabricated perovskite-based semiconductors that emit light when electrified. Their test LEDs demonstrated brightness and efficiency comparable to conventional LEDs. Encouraged by their results, they scaled down the LEDs further, maintaining performance and affordability. Ultimately, they achieved a pixel just 90 nanometers wide—equivalent to the size of a virus—with an astonishing pixel density of 127,000 pixels per inch.
Despite this breakthrough, challenges remain. The current perovskite LEDs are monochrome, requiring further research to enable full-color displays. Additionally, their long-term durability in real-world applications remains uncertain.
The team acknowledges that there is a limit to how small pixels can be before they become imperceptible to the human eye. Nevertheless, ultra-small LEDs could find applications in advanced technologies, such as augmented reality devices requiring extremely high resolution.


![[5G & 2.4G] Indoor/Outdoor Security Camera for Home, Baby/Elder/Dog/Pet Camera with Phone App, Wi-Fi Camera w/Spotlight, Color Night Vision, 2-Way Audio, 24/7, SD/Cloud Storage, Work w/Alexa, 2Pack](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/71gzKbvCrrL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)



![[3 Pack] Sport Bands Compatible with Fitbit Charge 5 Bands Women Men, Adjustable Soft Silicone Charge 5 Wristband Strap for Fitbit Charge 5, Large](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/61Tqj4Sz2rL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)