Check out our latest products
See how this smart fuse design replaces standard fuses with a semiconductor solution, allowing resettable protection, lower power use, and safety for vehicles.
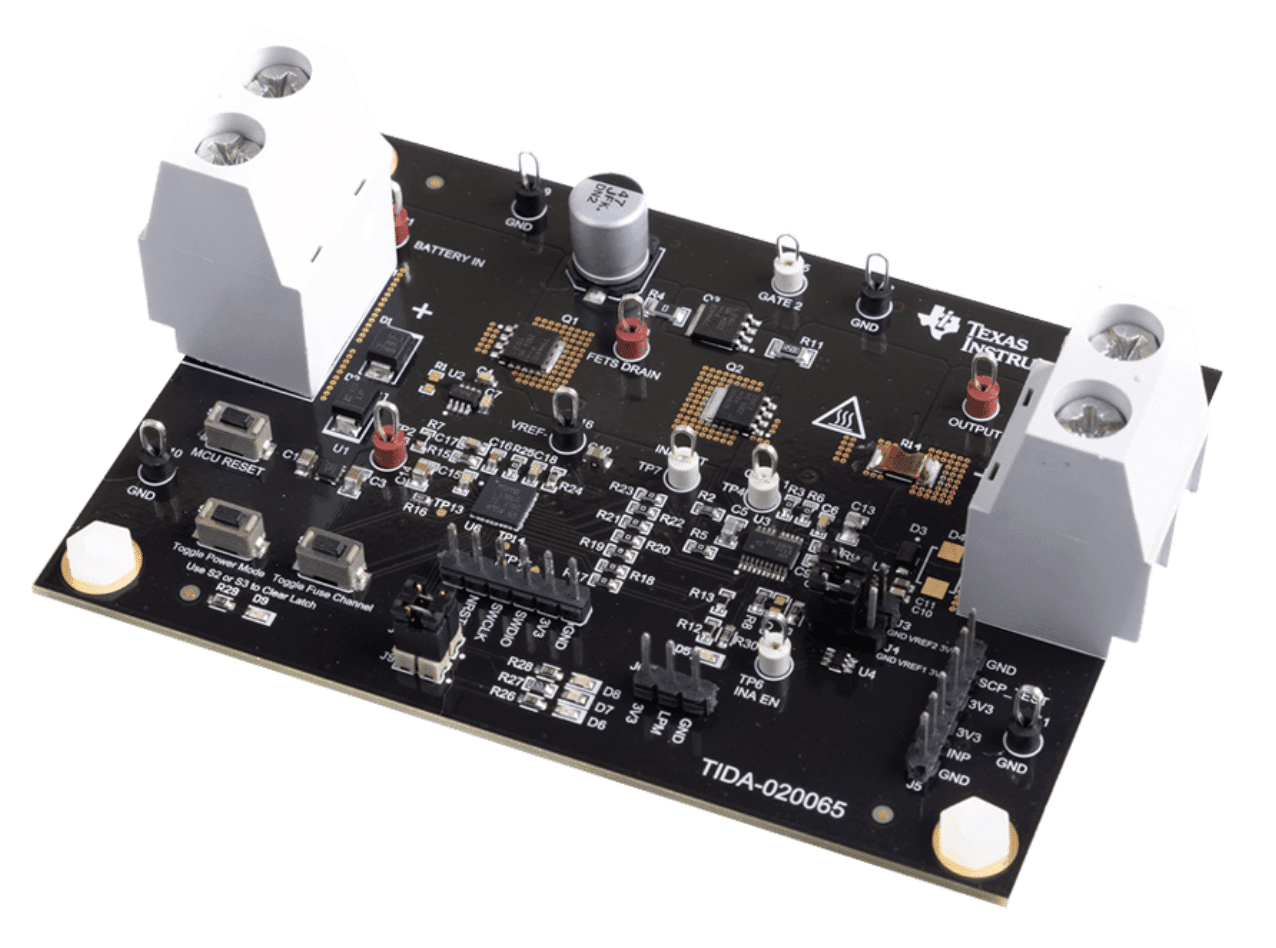
TIDA-020065, reference design from Texas Instruments (TI) addresses challenges in replacing standard melting fuses. It uses the TPS1213-Q1 high-side switch controller, INA296B-Q1 current sense amplifier, and a microcontroller to provide I²t overcurrent protection, a low-power mode for reduced energy consumption, and support for resistive, capacitive, and inductive loads. With multiple configuration options, including bidirectional current sensing, it enables engineers to conduct various tests for high-current smart fuse applications. The design is suitable for applications such as 12V and 48V power distribution boxes and zone control modules.
The design is built for power distribution boxes and zone control modules, supporting the transition from domain-based to zone-based vehicle architectures. By replacing standard melting fuses with semiconductor designs, it enables resettable fuses, eliminating the need for easily accessible fuse locations and allowing for optimized cable wiring. Additionally, it improves time-current characteristics across temperatures, reducing harness cable diameter and overall cost by minimizing device variability compared to traditional fuses.

However, replacing melting fuses introduces challenges such as ensuring wire harness protection during overload and short-circuit events while preventing trips during peak load transients, safeguarding FETs from uncontrolled inrush currents when charging load bulk capacitors, and reducing semiconductor power consumption in the key-off state for always-on loads. The design addresses these challenges at a system level for high-current loads by using the high-side switch controller to drive the main power path in the drive state and a low-power path in the key-off state. It also incorporates the current sense amplifier for load current sensing, enabling the MSPM0L1306-Q1 to execute a software-based I²t algorithm that replicates fuse behavior.
When considering vehicle states, the low-power path functions similarly to a parked (key-off) mode, minimizing power consumption. During driving, ECUs operate in normal mode, requiring the main path to support and protect higher current loads. The switch controller includes an automatic load wake-up feature, which quickly switches from low-power to active mode when the load current surpasses a configurable threshold. To further reduce system IQ in low-power mode, the TPS22919-Q1 load switch disables the current sense amplifier. Additionally, a gate slew-rate limiting circuit on the low-power path’s gate ensures controlled charging of capacitive loads at startup, reducing inrush currents and preventing false shutdowns caused by predefined time-current characteristics.

For overload and short-circuit protection, the INA296B-Q1 and MSPM0L1306-Q1 devices implement the I²t fuse algorithm. The current sense amplifier provides precise current sensing, sending data to an ADC in the MSPM0L1306-Q1, which continuously monitors current in active mode. If an overload occurs, the software-based I²t algorithm shuts down the output to protect wire harnesses and loads. Short-circuit protection is also built into the design through the switch controller, which monitors the VDS of the main FET and triggers a fault when VDS exceeds a configurable threshold.
TI has tested this reference design. It comes with a bill of materials (BOM), schematics, assembly drawing, printed circuit board (PCB) layout, and more. The company’s website has additional data about the reference design. To read more about this reference design, click here.


![[5G & 2.4G] Indoor/Outdoor Security Camera for Home, Baby/Elder/Dog/Pet Camera with Phone App, Wi-Fi Camera w/Spotlight, Color Night Vision, 2-Way Audio, 24/7, SD/Cloud Storage, Work w/Alexa, 2Pack](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/71gzKbvCrrL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)



![[3 Pack] Sport Bands Compatible with Fitbit Charge 5 Bands Women Men, Adjustable Soft Silicone Charge 5 Wristband Strap for Fitbit Charge 5, Large](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/I/61Tqj4Sz2rL._AC_SL1500_.jpg)